Table des matières
Programmer le GPIO avec Python
Connexion au Raspberry
Il y a deux manières de travailler en mode commande (cli) avec le Raspberry :
- en local en connectant un écran et un clavier (éventuellement une souris) et ouvrir un terminal,
- à distance en utilisant SSH :
- le Rapsberry doit être connecté au réseau en filaire ou en wifi,
- utiliser son propre ordinateur avec un client ssh :
- Putty sous Windows,
- le terminal et la commande ssh pour Linux et Mac OsX.
ssh pi@adressIPduRaspberry
- en installant un client Samba sur le Raspberry, il est également possible de partager un dossier et d'y accéder avec le protocole SMB comme s'il s'agissait du partage d'un ordinateur Windows
- Le compte existant est pi,
- le mot de passe est raspberry
Passer root
Pour passer root afin d'effectuer une série de tâches d'administration, utilise zla commande suivante :
$ sudo su #
Pour redenir l'utilisateur pi :
# exit
Arrêter/redémarrer le Raspberry
- arrêter le Raspberry
$ sudo halt $ sudo shutdown -h now
- redémarrer le Raspberry <code shell> $ sudo reboot </code>
Tutoriels
Installer l'environnement Python 3 + les bibliothèques nécessaires
- Mettre à jour le système d'exploitation Rasbian
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade
- installer Python 3
$ sudo apt install python3 $ sudo apt install python3-pip
* installer la bibliothèque RPi.GPIO
$sudo pip3 install RPi.GPIO
Programmer le GPIO
Ressources :
Le programme python doit :
- importer la bibliothèque RPi.GPIO
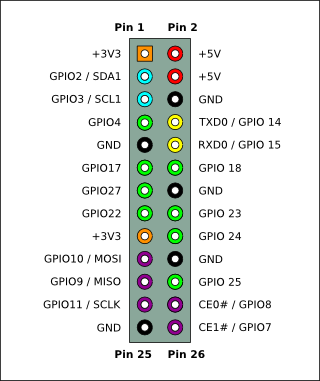
- définir quelles sont les broches (pin) utilisées en entrée ou en sortie et les initialiser
- utiliser les broches :
- en entrée en testant leur valeur
- en sortie activer ou désactiver les broches
- à la fin du programme remettre à zero les entrees-sorties numériques
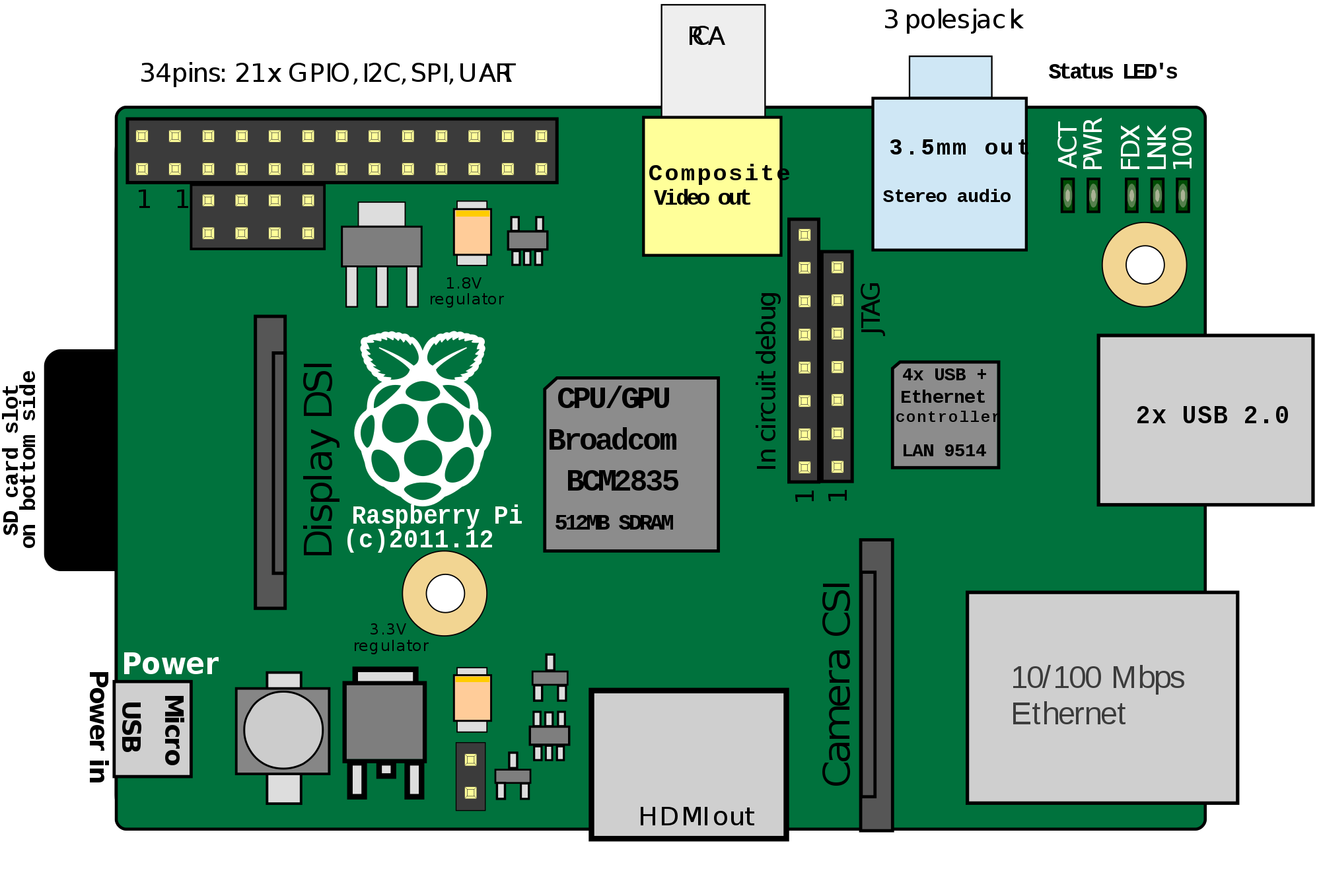
Raspberry Model B P1
Exemple pour gérer un chenillard de 3 LEDs
#!/usr/bin/python #importation des bibliothèques import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time #Initialisation des broches du GPIO et temporisation GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) rouge=23 vert=24 orange=25 LED_list = (rouge,vert,orange) GPIO.setup(LED_list, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW) duree=0.5 #chenillard for i in range(3): # definir pour chaque LED de la liste son état : HIGH (allumée), LOW (éteinte) #commande équivalente à 3 instructions #GPIO.output(rouge,GPIO.HIGH) #GPIO.output(vert,GPIO.LOW) #GPIO.output(orange,GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(LED_list,(GPIO.HIGH,GPIO.LOW, GPIO.LOW)) time.sleep(duree) GPIO.output(LED_list,(GPIO.LOW, GPIO.HIGH, GPIO.LOW)) time.sleep(duree) GPIO.output(LED_list,(GPIO.LOW,GPIO.LOW, GPIO.HIGH)) time.sleep(duree) #reset du GPIO GPIO.cleanup()